Category Archives: XBeach
Storm-Driven Erosion and Inundation of Barrier Islands from Dune- to Region-Scales
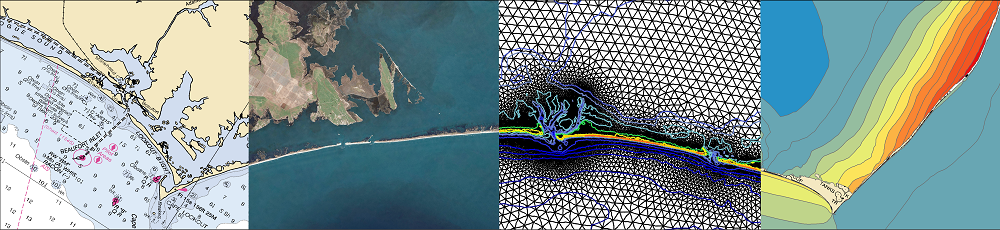
 Barrier islands are susceptible to erosion, overwash, and breaching during intense storms. However, these processes are not represented typically in large-domain models for storm surge and coastal inundation. In this study, we explore the requirements for bridging the gap between dune-scale morphodynamic and region-scale flooding models. A high-resolution XBeach model is developed to represent the morphodynamics during Hurricane Isabel (2003) in the North Carolina (NC) Outer Banks. The model domain is extended to more than 30 km of Hatteras Island and is thus larger than in previous studies. The predicted dune erosion is in good agreement with post-storm observed topography, and an ‘‘excellent’’ Skill Score of 0.59 is obtained on this large domain. Sensitivity studies show the morphodynamic model accuracy is decreased as the mesh spacing is coarsened in the cross-shore direction, but the results are less sensitive to the alongshore resolution. A new metric to assess model skill, Water Overpassing Area (WOA), is introduced to account for the available flow pathway over the dune crest. Together, these findings allow for upscaled parameterizations of erosion in larger-domain models. The updated topography, obtained from XBeach prediction, is applied in a region-scale flooding model, thus allowing for enhanced flooding predictions in communities along the Outer Banks. It is found that, even using a fixed topography in region-scale model, the flooding predictions are improved significantly when post-storm topography from XBeach is implemented. These findings can be generalized to similar barrier island systems, which are common along the U.S. Gulf and Atlantic coasts.
Barrier islands are susceptible to erosion, overwash, and breaching during intense storms. However, these processes are not represented typically in large-domain models for storm surge and coastal inundation. In this study, we explore the requirements for bridging the gap between dune-scale morphodynamic and region-scale flooding models. A high-resolution XBeach model is developed to represent the morphodynamics during Hurricane Isabel (2003) in the North Carolina (NC) Outer Banks. The model domain is extended to more than 30 km of Hatteras Island and is thus larger than in previous studies. The predicted dune erosion is in good agreement with post-storm observed topography, and an ‘‘excellent’’ Skill Score of 0.59 is obtained on this large domain. Sensitivity studies show the morphodynamic model accuracy is decreased as the mesh spacing is coarsened in the cross-shore direction, but the results are less sensitive to the alongshore resolution. A new metric to assess model skill, Water Overpassing Area (WOA), is introduced to account for the available flow pathway over the dune crest. Together, these findings allow for upscaled parameterizations of erosion in larger-domain models. The updated topography, obtained from XBeach prediction, is applied in a region-scale flooding model, thus allowing for enhanced flooding predictions in communities along the Outer Banks. It is found that, even using a fixed topography in region-scale model, the flooding predictions are improved significantly when post-storm topography from XBeach is implemented. These findings can be generalized to similar barrier island systems, which are common along the U.S. Gulf and Atlantic coasts.
Virtual Conference: ADCIRC 2020
Posters: EWC Symposium 2020
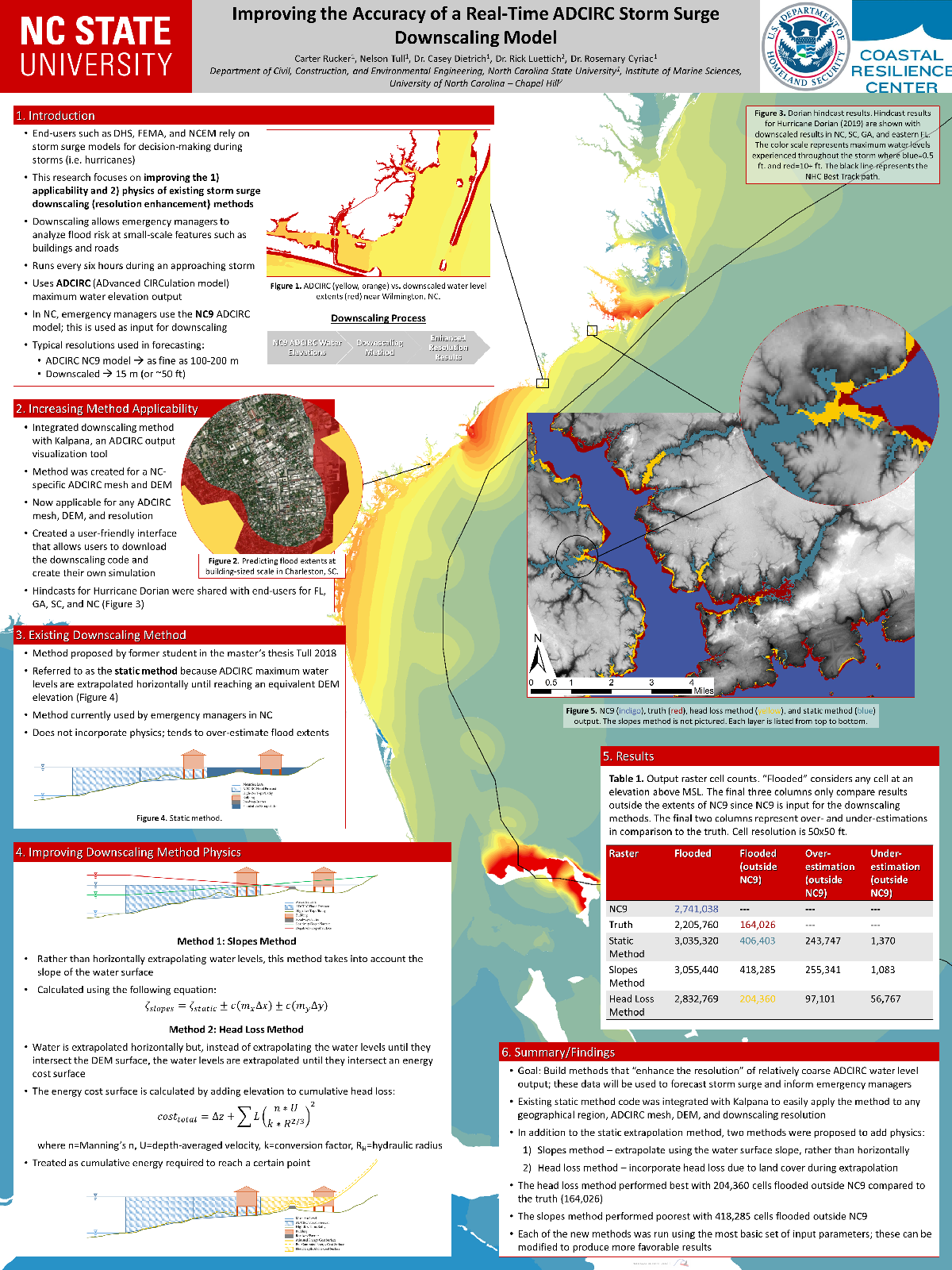
CA Rucker, N Tull, JC Dietrich, R Luettich, R Cyriac. “Improving the accuracy of a real-time ADCIRC storm surge downscaling model.” Environmental, Water Resources, and Coastal Engineering Research Symposium , North Carolina State University, 6 March 2020.
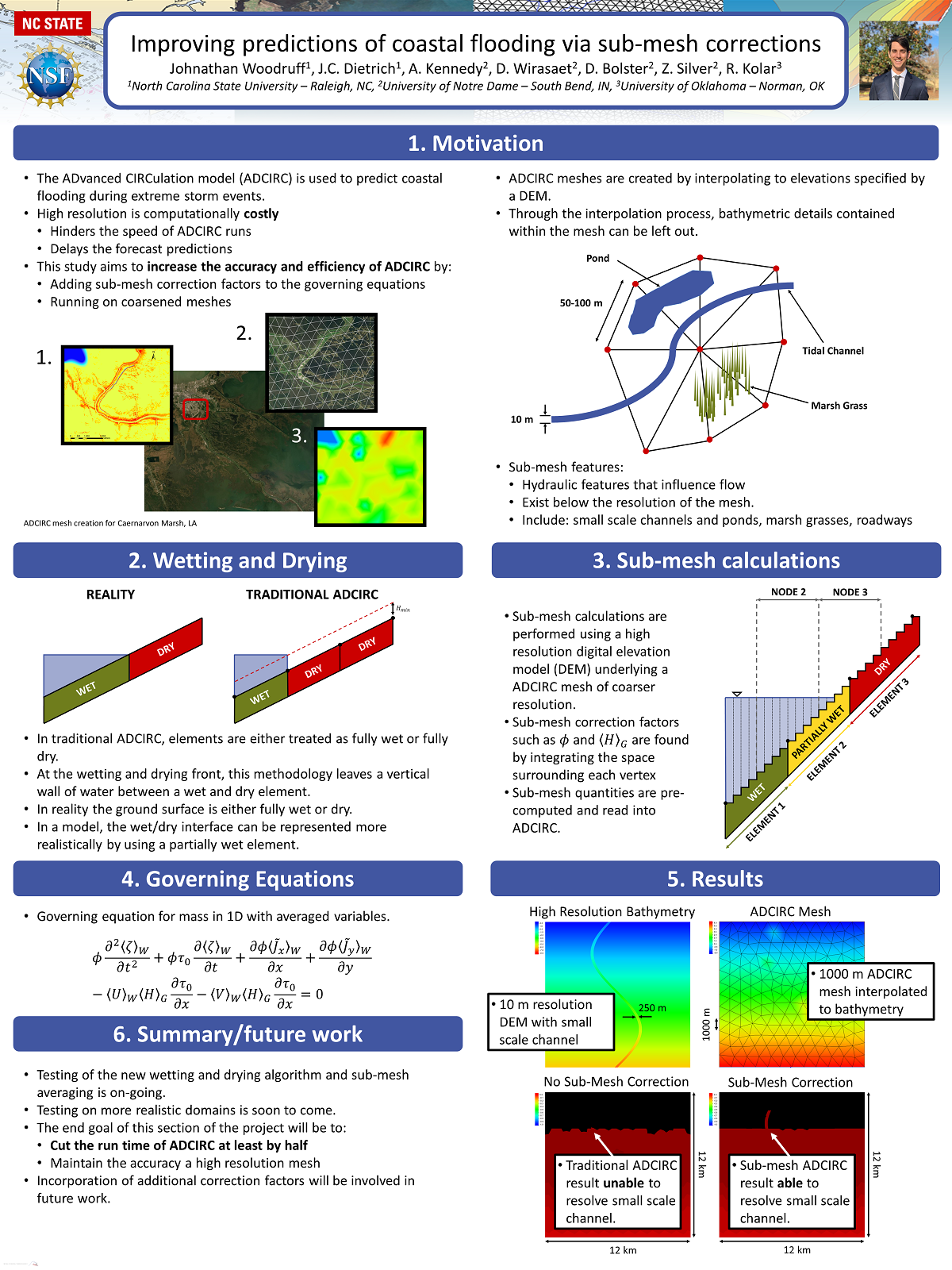
JL Woodruff, JC Dietrich, AB Kennedy, D Wirasaet, D Bolster, Z Silver, RL Kolar. “Improving predictions of coastal flooding via sub-mesh corrections.” Environmental, Water Resources, and Coastal Engineering Research Symposium, North Carolina State University, 6 March 2020.
Seminar: UNC Wilmington
Conference: ASBPA Coastal Conference 2019
Sustainability of Barrier Island Protection Policies under Changing Climates
A stochastic climate emulator will first be developed to simulate 1000s of realizations of chronological climate patterns (forced by satellite and GCM products) to create future storm events coupled with sea level rise scenarios. A library of high fidelity, open source, hydrodynamic and morphodynamic simulations (ADCIRC+SWAN and XBeach) will then be used to develop a surrogate model to predict erosion and flooding for each future realization. Triggers like beach width, dune height, and community preferences will be used to identify how often communities will need to re-nourish, contingent on future climate and sea level rise scenario.
JC Dietrich, DL Anderson. “Sustainability of Barrier Island Protection Policies under Changing Climates.” U.S. Coastal Research Program, 2019 Academic Research Opportunities, 2019/10/18 to 2021/10/17, $226,624 (Dietrich: $226,624).