Category Archives: Projects
Poster: Fall 2023 Conferences
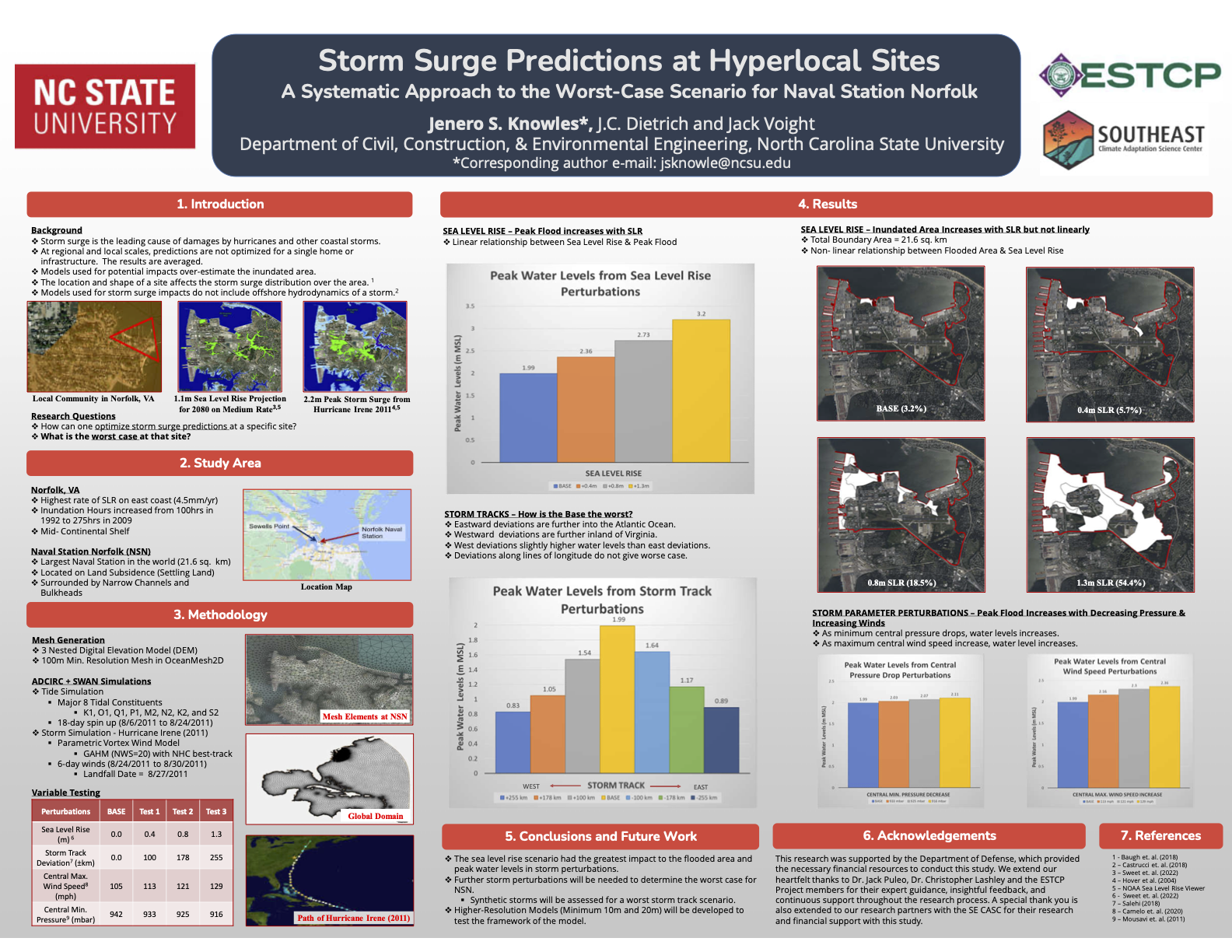
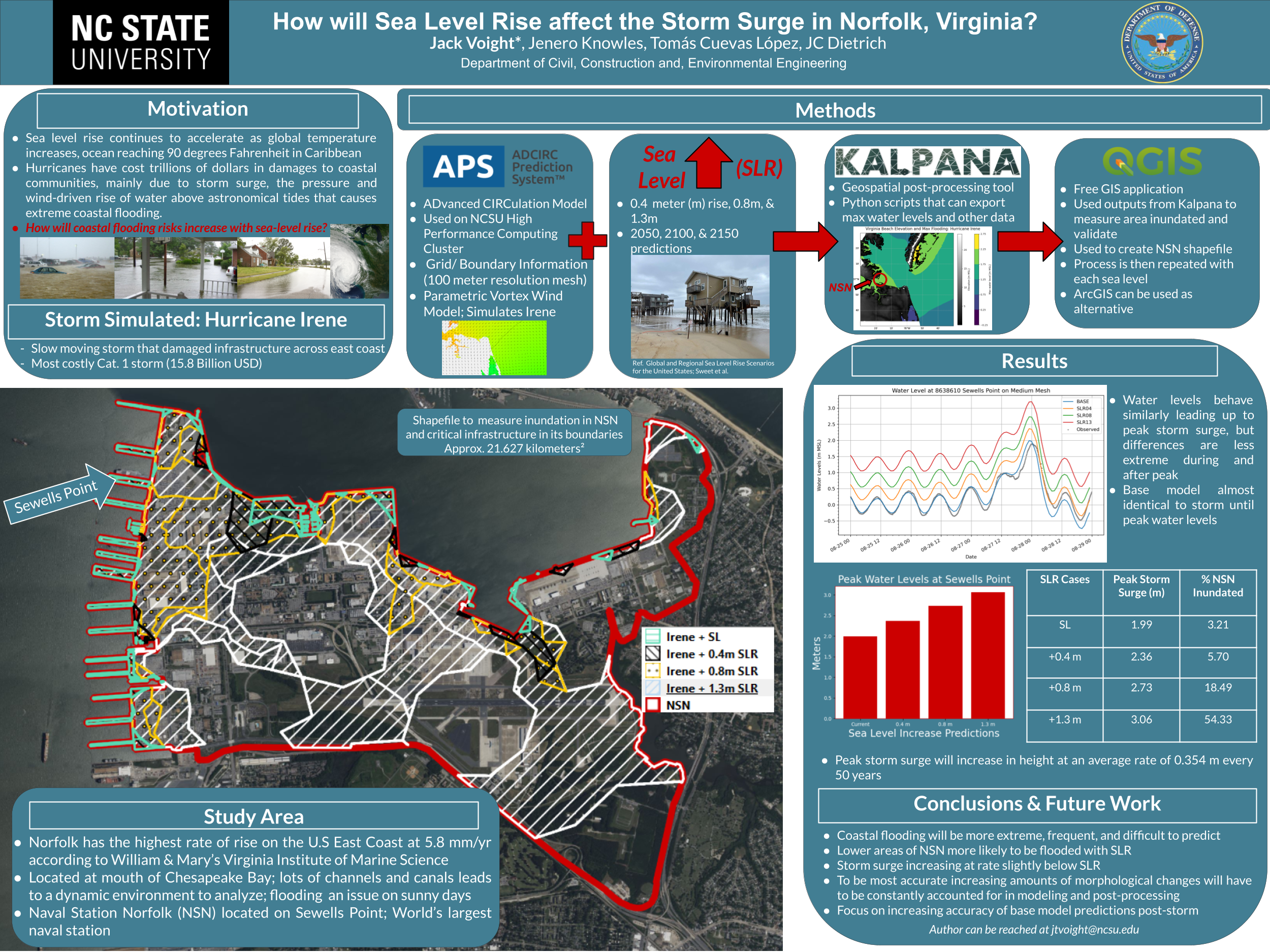
Storm Surge Predictions at Hyperlocal Sites
Efficiency Gains for Spectral Wave Models in Coupled Frameworks
Thus, there are remaining research questions related to how to improve the performance of a spectral wave model in a coupled modeling framework. What are the tradeoffs when a spectral wave model is nested nearshore and receives boundary conditions from other sources? Over what period should the spectral wave model simulate as a storm approaches a coast? Can this research lead to guidance or best practices for coupled modeling applications? This project will focus on the Simulating WAves Nearshore (SWAN) model and SWAN+ADCIRC framework, but the project findings will be transferable to other spectral wave models and frameworks. We aim to improve the ability to nest spectral wave models in both space and time, via modernization of boundary conditions and a coupled model controller, and thus improve computational efficiency.
JC Dietrich. “Efficiency gains for spectral wave models in coupled frameworks.” Department of Defense, Broad Agency Announcement, Engineer Research and Development Center, Coastal Hydraulics Laboratory, 2023/09/22 to 2025/09/21, $191,353 (Dietrich: $191,353).
Poster: Undergraduate Research Symposium 2023
Conference: USNCCM 17
Subgrid Corrections in Storm-Driven Coastal Flooding
 In this dissertation, subgrid corrections have been added to the ADvanced CIRCulation (ADCIRC) model, a widely used, continuous-Galerkin finite-element based, shallow water flow model. This includes the full derivation of averaged governing equations, closure approximations, and subgrid implementation into the source code. Testing of this new model was first performed on 3 domains: an idealized winding channel, a tidally influenced bay in Massachusetts, and a regional storm surge model covering Calcasieu Lake in Southwestern Louisiana with forcing from Rita (2005). By pre-computing the averaged variables from high-resolution bathy/topo data sets, the model can represent hydraulic connectivity at smaller scales. This allows for a coarsening of the model and thus faster predictions of flooding, while also improving accuracy. The implementation permits changing a logic-based wetting and drying algorithm to a more desirable logic-less algorithm, and requires averaging correction factors on both an elemental and vertex basis. This new framework further increases efficiency of the model, and is general enough to be used in other Galerkin-based, finite-element, hydrodynamic models. It is shown that the flooding model with subgrid corrections can match the accuracy of the conventional model, while offering a 10 to 50 times increase in speed.
In this dissertation, subgrid corrections have been added to the ADvanced CIRCulation (ADCIRC) model, a widely used, continuous-Galerkin finite-element based, shallow water flow model. This includes the full derivation of averaged governing equations, closure approximations, and subgrid implementation into the source code. Testing of this new model was first performed on 3 domains: an idealized winding channel, a tidally influenced bay in Massachusetts, and a regional storm surge model covering Calcasieu Lake in Southwestern Louisiana with forcing from Rita (2005). By pre-computing the averaged variables from high-resolution bathy/topo data sets, the model can represent hydraulic connectivity at smaller scales. This allows for a coarsening of the model and thus faster predictions of flooding, while also improving accuracy. The implementation permits changing a logic-based wetting and drying algorithm to a more desirable logic-less algorithm, and requires averaging correction factors on both an elemental and vertex basis. This new framework further increases efficiency of the model, and is general enough to be used in other Galerkin-based, finite-element, hydrodynamic models. It is shown that the flooding model with subgrid corrections can match the accuracy of the conventional model, while offering a 10 to 50 times increase in speed.
 Next, higher level corrections to bottom friction and advection were incorporated into the subgrid model, and the framework was expanded and tested at the ocean-scale. It was hypothesized that by adding higher-level corrections to the model and applying them to ocean-scale domains, accurate predictions of storm surge at the smallest coastal scales can be obtained. To accomplish this, higher-level corrections were derived and implemented into the governing equations and extensive elevation and landcover data sets were curated to cover the South Atlantic Bight region of the U.S. Atlantic Coast. From there, the subgrid model was tested on an ocean-scale domain with tidal and meteorological forcing from Matthew (2016). The improvements in water level prediction accuracy due to subgrid corrections are evaluated at 218 observation locations throughout 1500 km of coast along the South Atlantic Bight. The accuracy of the subgrid model with relatively coarse spatial resolution (RMSE = 0.41 m) is better than that of a conventional model with relatively fine spatial resolution (RMSE = 0.67 m).By running on the coarsened subgrid model, we improved the accuracy over efficiency curve for the model, and as a result the computational expense of the simulation was decreased by a factor of 13.
Next, higher level corrections to bottom friction and advection were incorporated into the subgrid model, and the framework was expanded and tested at the ocean-scale. It was hypothesized that by adding higher-level corrections to the model and applying them to ocean-scale domains, accurate predictions of storm surge at the smallest coastal scales can be obtained. To accomplish this, higher-level corrections were derived and implemented into the governing equations and extensive elevation and landcover data sets were curated to cover the South Atlantic Bight region of the U.S. Atlantic Coast. From there, the subgrid model was tested on an ocean-scale domain with tidal and meteorological forcing from Matthew (2016). The improvements in water level prediction accuracy due to subgrid corrections are evaluated at 218 observation locations throughout 1500 km of coast along the South Atlantic Bight. The accuracy of the subgrid model with relatively coarse spatial resolution (RMSE = 0.41 m) is better than that of a conventional model with relatively fine spatial resolution (RMSE = 0.67 m).By running on the coarsened subgrid model, we improved the accuracy over efficiency curve for the model, and as a result the computational expense of the simulation was decreased by a factor of 13.
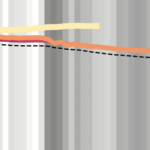 Finally, subgrid corrections were systematically tested on a series of five ocean-scale meshes with minimum nearshore resolutions ranging from around 60 m on the highest resolution mesh to 1000 m on the coarsest mesh. This study aimed to find the mesh resolution that offered the best trade-off between accuracy and efficiency. The limitations of the subgrid model were explored and guidelines for future users were established. In all, it was found that the primary limitation to the subgrid model came from the aliasing of important flow-blocking features such as barrier islands in the coarsest resolution meshes. However, in areas without these features subgrid corrections can offer tremendous advantages while running on very coarse meshes.
Finally, subgrid corrections were systematically tested on a series of five ocean-scale meshes with minimum nearshore resolutions ranging from around 60 m on the highest resolution mesh to 1000 m on the coarsest mesh. This study aimed to find the mesh resolution that offered the best trade-off between accuracy and efficiency. The limitations of the subgrid model were explored and guidelines for future users were established. In all, it was found that the primary limitation to the subgrid model came from the aliasing of important flow-blocking features such as barrier islands in the coarsest resolution meshes. However, in areas without these features subgrid corrections can offer tremendous advantages while running on very coarse meshes.
The work completed in this dissertation moves the science of subgrid corrections forward by integrating the corrections into a widely used ocean-circulation and storm surge model. This work offers improvements to both hurricane storm surge forecasting and long-term design by allowing for reduced run-times and increased accuracy on coarsened numerical meshes.
Deterministic, Dynamic Model Forecasts of Storm-Driven Erosion
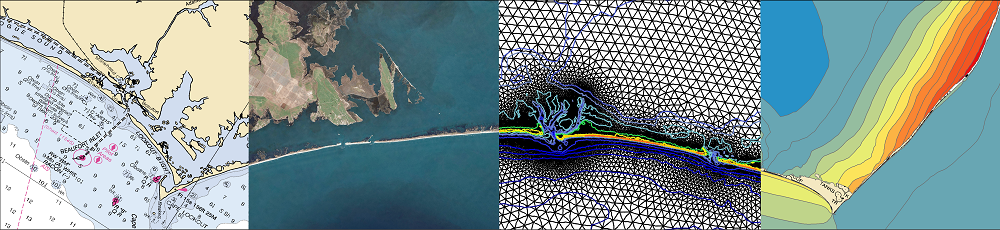
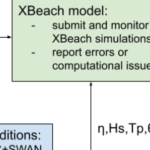 In this study, we apply the state-of-art model eXtreme Beach (XBeach) to predict coastal erosion due to Hurricanes Michael (2018) and Ian (2022). Sandy beaches along the U.S. Atlantic and Gulf coasts are represented with thousands of one-dimensional transects, which are sampled for real-time forecasts based on the storms’ tracks and projected landfall locations. The morphodynamic model is initialized with high-resolution digital elevation models of the present-day conditions and forced with hydrodynamics from high-resolution wave and circulation models, and its predictions are categorized based on impacts to the primary dune. A key contribution of this study is the semi-automation of the modeling system, so the modeling framework can be applied to different regions of the coast as the landfall location shifts.
In this study, we apply the state-of-art model eXtreme Beach (XBeach) to predict coastal erosion due to Hurricanes Michael (2018) and Ian (2022). Sandy beaches along the U.S. Atlantic and Gulf coasts are represented with thousands of one-dimensional transects, which are sampled for real-time forecasts based on the storms’ tracks and projected landfall locations. The morphodynamic model is initialized with high-resolution digital elevation models of the present-day conditions and forced with hydrodynamics from high-resolution wave and circulation models, and its predictions are categorized based on impacts to the primary dune. A key contribution of this study is the semi-automation of the modeling system, so the modeling framework can be applied to different regions of the coast as the landfall location shifts.
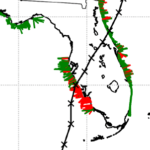 To demonstrate this, forecasts for Ian (2022) were initiated several days before the initial landfall location in Punta Gorda, Florida, and continued as the track made a secondary landfall near Georgetown, South Carolina. About 1800 transects are selected for each of the 25 advisories. The simulations are monitored, evaluated, and visualized to communicate the XBeach predictions of coastal change. The framework produces results in less than an hour and then publishes visualizations in less than 10 minutes. Results are compared spatially and temporally to qualitative post-Ian observations and total water level predictions. XBeach can predict dune impact compared to an established coastal change forecasting model while providing additional morphodynamic information not typically available, such as timing and magnitude of volume change. The addition of fully resolved ground surface information and morphodynamics in the model makes it possible to better understand the storm evolution and how that translates into erosion of beaches and dunes.
To demonstrate this, forecasts for Ian (2022) were initiated several days before the initial landfall location in Punta Gorda, Florida, and continued as the track made a secondary landfall near Georgetown, South Carolina. About 1800 transects are selected for each of the 25 advisories. The simulations are monitored, evaluated, and visualized to communicate the XBeach predictions of coastal change. The framework produces results in less than an hour and then publishes visualizations in less than 10 minutes. Results are compared spatially and temporally to qualitative post-Ian observations and total water level predictions. XBeach can predict dune impact compared to an established coastal change forecasting model while providing additional morphodynamic information not typically available, such as timing and magnitude of volume change. The addition of fully resolved ground surface information and morphodynamics in the model makes it possible to better understand the storm evolution and how that translates into erosion of beaches and dunes.