Category Archives: DOD ESTCP 2022-2026
Posters: EWC Symposium 2025
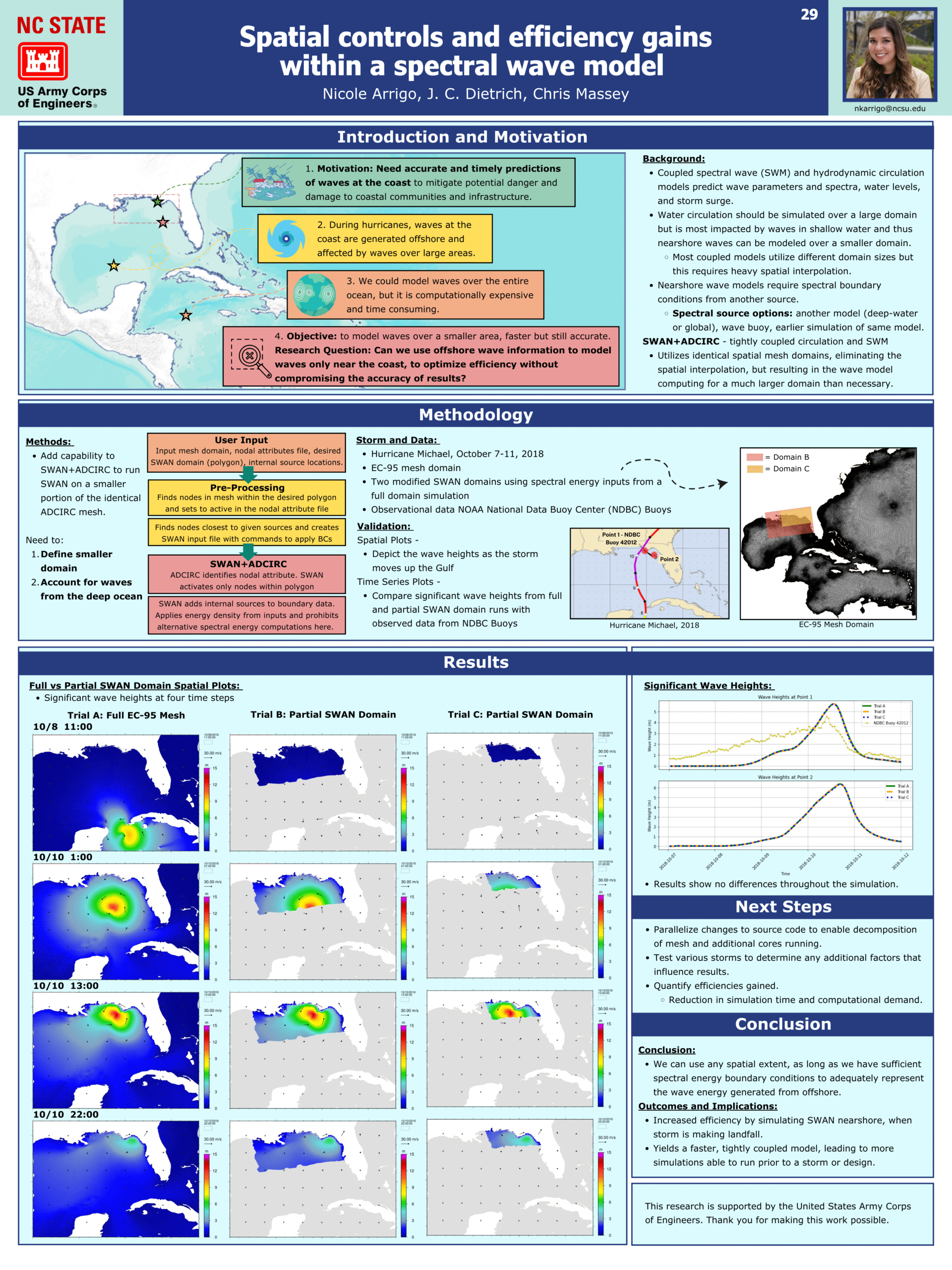
Spatial controls and efficiency gains within a spectral wave model.
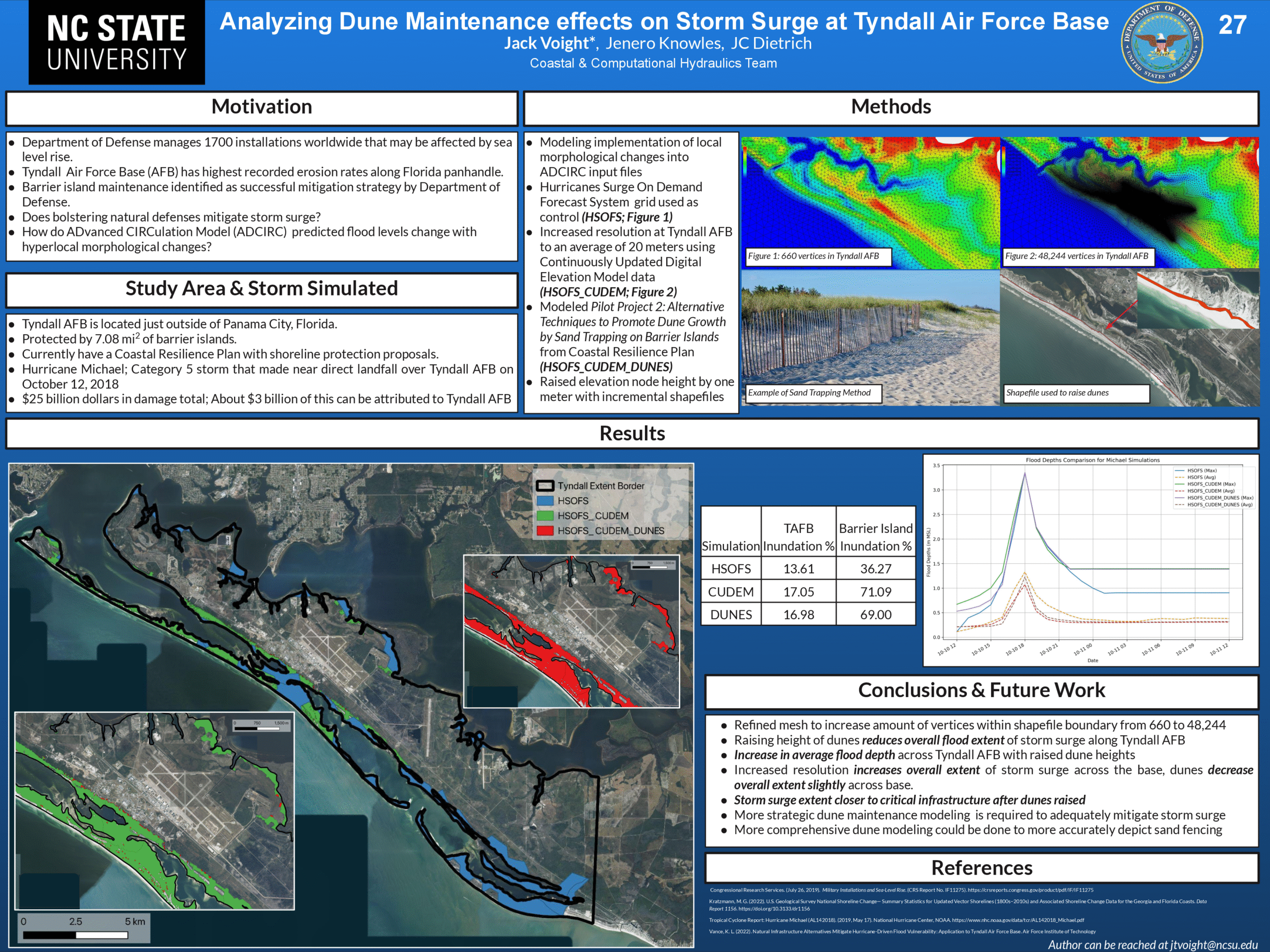
Analyzing Dune Maintenance effects on Storm Surge at Tyndall Air Force Base.
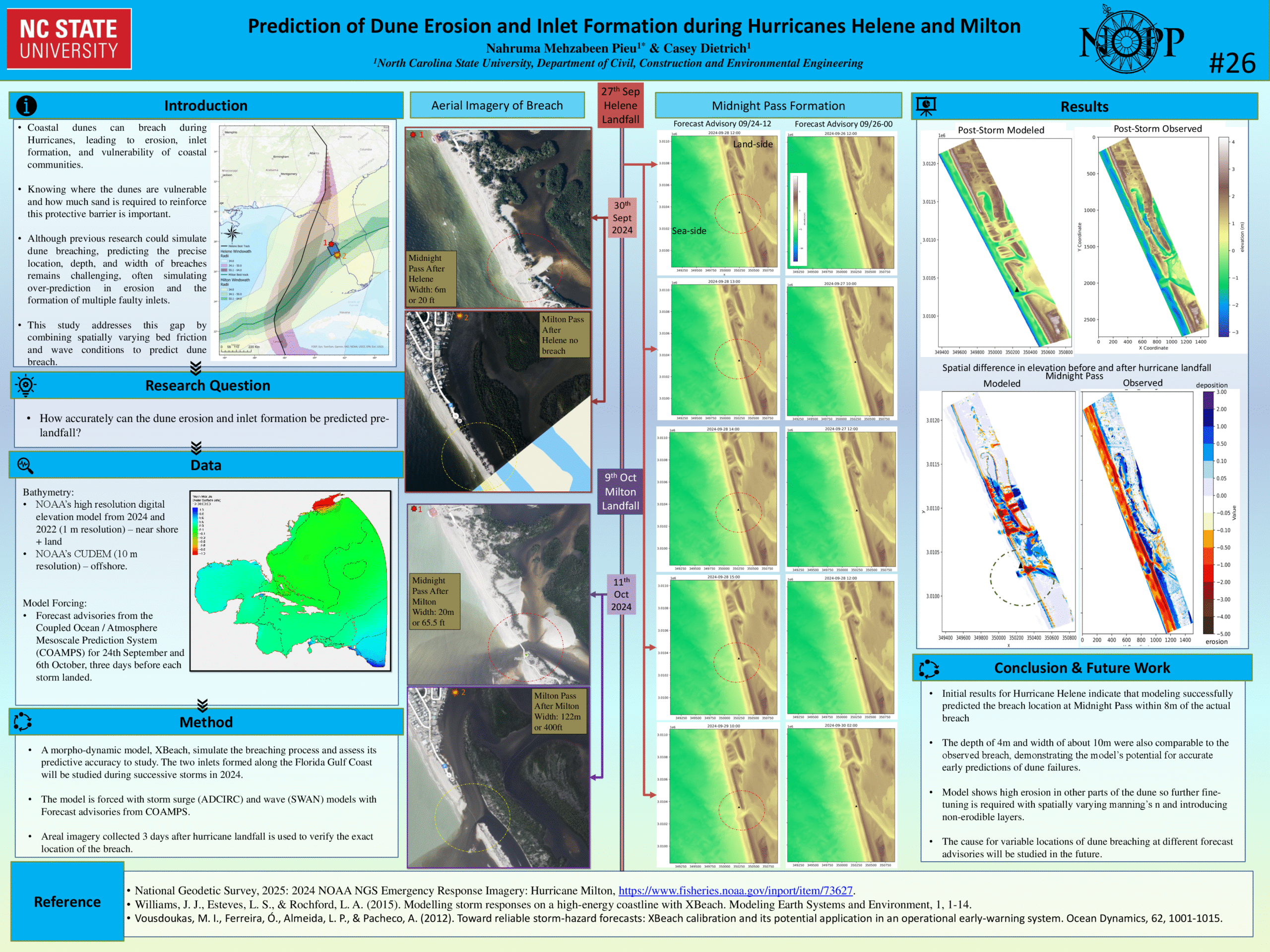
Prediction of Dune Erosion and Inlet Formation during Hurricanes Helene and Milton.
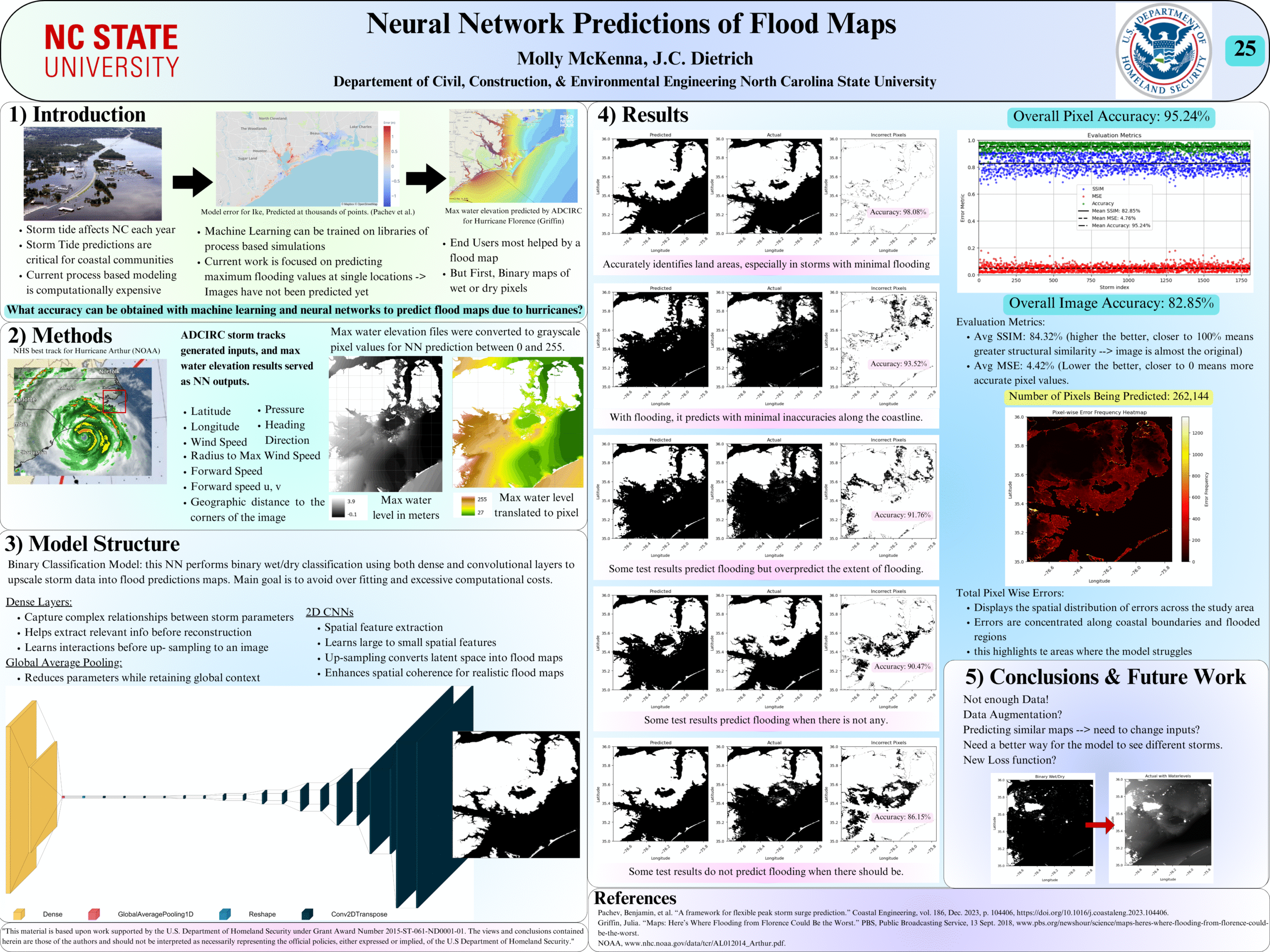
Neural Network Predictions of Flood Maps
Sensitivity of Water Level and Flood Area Prediction to Hurricane Characteristics and Climate Change Impacts
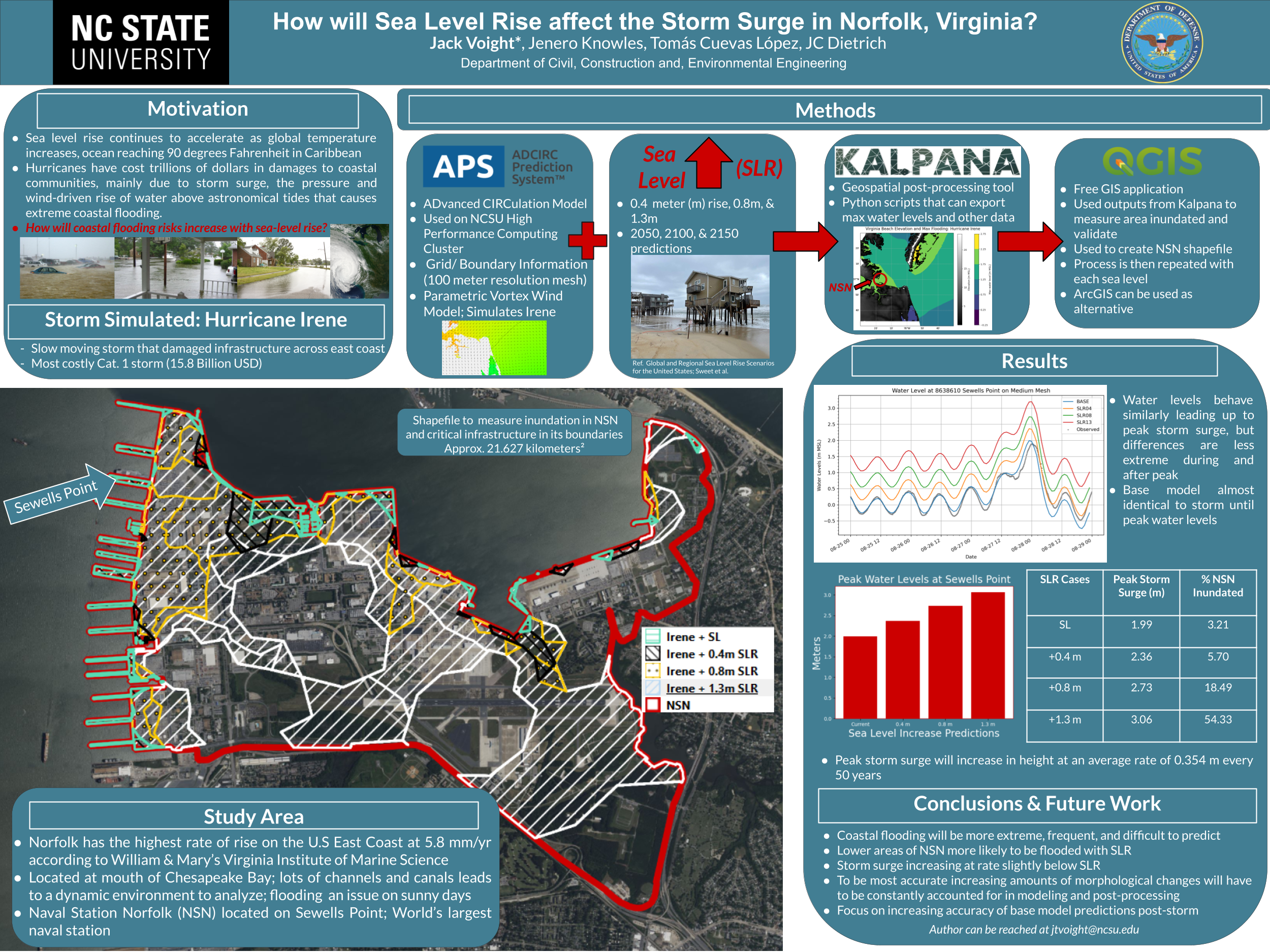
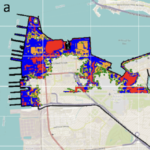 The combined impact of hurricanes and climate change can affect the total water level leading to severe impacts on coastal zones such as flooding. Accurate prediction and evaluation of water levels are essential for predicting the impact on military readiness and resilience for coastal facilities. This study uses D-Flow Flexible Mesh to evaluate the sensitivity of water level and flood area prediction to the impact of climate change and hurricane activity with application to the Naval Station Norfolk, Virginia, USA.
The combined impact of hurricanes and climate change can affect the total water level leading to severe impacts on coastal zones such as flooding. Accurate prediction and evaluation of water levels are essential for predicting the impact on military readiness and resilience for coastal facilities. This study uses D-Flow Flexible Mesh to evaluate the sensitivity of water level and flood area prediction to the impact of climate change and hurricane activity with application to the Naval Station Norfolk, Virginia, USA.
The water level (tide and surge) was simulated and the potential flooding resulting from historical hurricanes (Irene and Isabel) in Norfolk, VA was evaluated. The model was forced using the parametric Holland Model and various perturbations in the hurricane characteristics were evaluated. In addition, projected relative sea level rise up to the year 2150 was investigated.
D-Flow can accurately simulate the water level with an average correlation coefficient and root-mean-square-error of 0.974 and 0.17 m, respectively. Water level prediction showed high sensitivity to climate change impacts and inaccuracies in hurricane track and lower sensitivity to changes in hurricane central pressure and radius of maximum wind. A mesh resolution that reflects accurate topographical depiction is required to estimate the flood area accurately. Willoughby Spit (a narrow peninsula north of the naval base extending into Chesapeake Bay) was the most susceptible area to flooding. Significant parts of the base were found to be vulnerable to flooding under the considered scenarios, with flood areas ranging from 0.28 km2 to 5.94 km2 (1.3%–43% of the base area), with the largest predicted flooding for the sea level rise and wind speed scenarios. The insights of the sensitivity of flood predictions to various factors could enable targeted adaptation measures and resource allocation, for enhanced resilience and sustainable development in vulnerable coastal areas.
Conference : YCSECA 2024
Conference: ADCIRC Users Meeting 2024
Poster: Fall 2023 Conferences
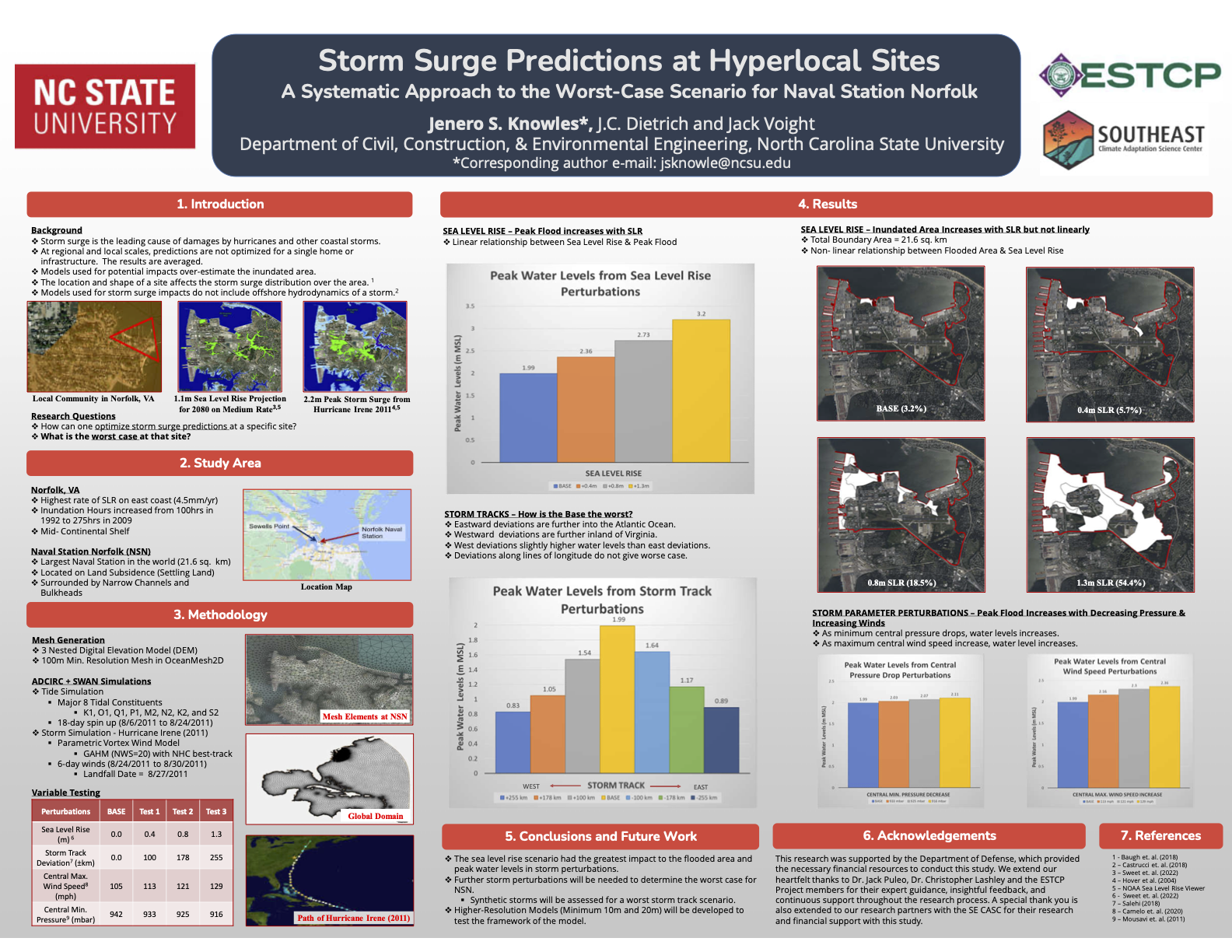
Storm Surge Predictions at Hyperlocal Sites