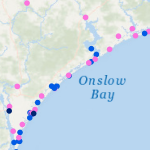
One of the most unpredictable and deadly parts of a coastal storm is the storm surge, which can cause devastating flooding of coastal regions, and can result in loss of property and life. Storm surge is a result of winds pushing water from the nearshore ocean to rise above regular tide levels. Storm surge can have a short duration; elevated water levels are limited to when the storm winds are strongest at the coast, typically for a few hours as the storm makes landfall. This short duration is a challenge for predictions of when storm surge will start, how long it will persist, and which regions will be flooded.
To predict storm surge and its associated flooding in coastal areas, numerical models must have a detailed representation of the impacted region, and thus be accurate, without having too much detail, which can limit efficiency. This research examines the use of a multi-resolution approach to improve both efficiency and accuracy. The key idea is that, as a storm travels across the ocean, it will affect different regions at different times. Early on, as the storm moves in open water and far from people, efficiency is more important in the model predictions. But as the storm moves toward the coast, it becomes necessary to have a higher accuracy near coastal communities and infrastructure. This research examines the use of multi-resolution simulations in which, as a storm travels along its track, the model ‘switches’ from lower resolution in open water to higher resolution as the storm moves closer to land. The main research question is to determine when is it most beneficial to switch resolutions by determining when storm effects are first seen at the coast.
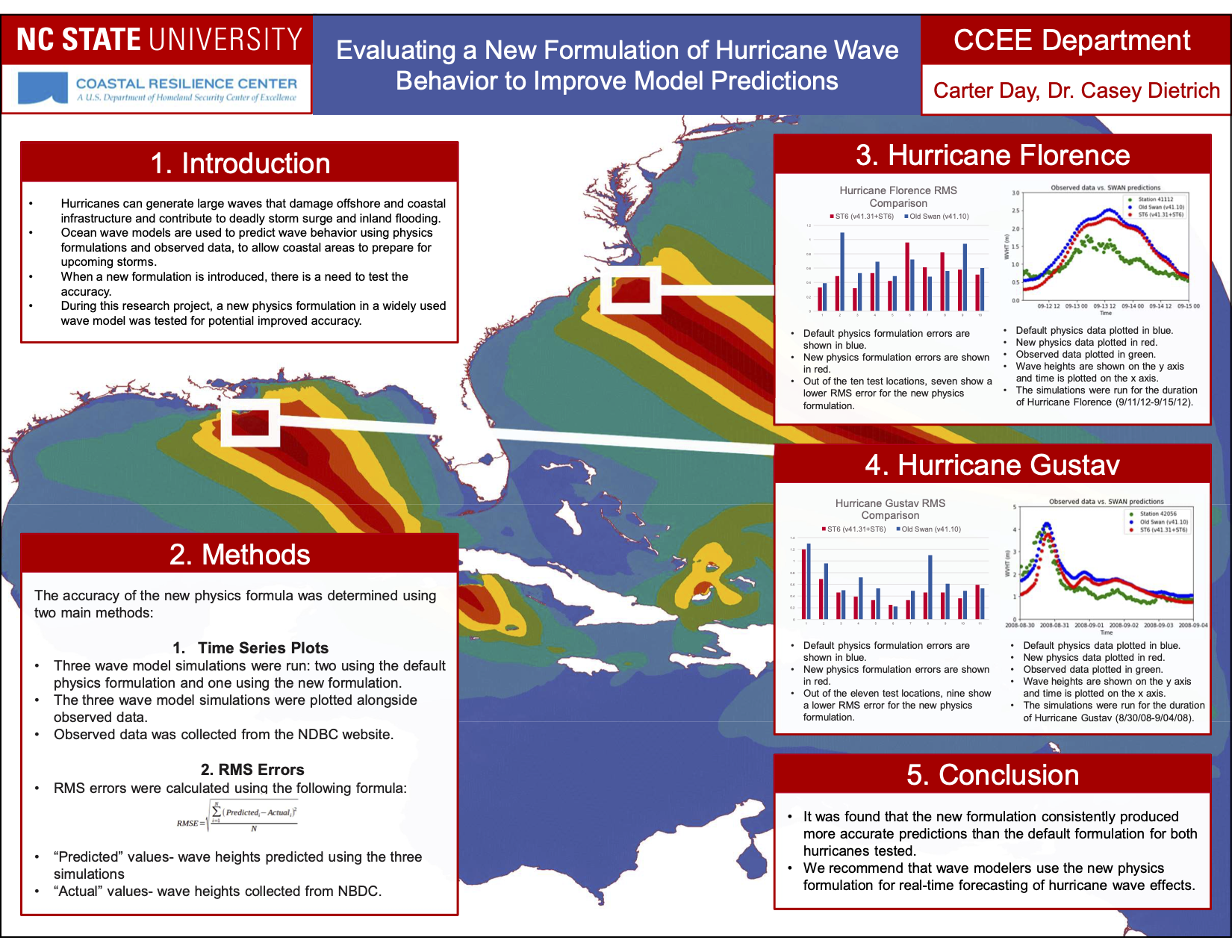
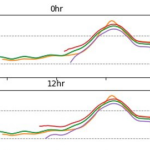 This research will explore the arrival of storm effects for Florence, which made landfall along the North Carolina coast during September 2018. It is an ideal storm for this research as its track was shore-normal, and thus its coastal effects increased as it approached landfall. This will allow for investigating the most optimal switch by focusing on a single switch between a lower-resolution mesh to a higher-resolution mesh. The switches will be initiated by several triggers, including wind speeds and water levels at the coast and inland locations, and with several lead times, including near and several days before landfall. Model performance will be quantified via comparisons to observations of storm effects in the region, as well as to a single, high-resolution simulation for the full storm. It will be shown that switching from a coarse resolution mesh to a fine resolution mesh will lead to an increase in efficiency gains across all switching simulations with the most optimal switch time resulting in the most accurate predictions of water levels as compared to our full high-resolution simulation.
This research will explore the arrival of storm effects for Florence, which made landfall along the North Carolina coast during September 2018. It is an ideal storm for this research as its track was shore-normal, and thus its coastal effects increased as it approached landfall. This will allow for investigating the most optimal switch by focusing on a single switch between a lower-resolution mesh to a higher-resolution mesh. The switches will be initiated by several triggers, including wind speeds and water levels at the coast and inland locations, and with several lead times, including near and several days before landfall. Model performance will be quantified via comparisons to observations of storm effects in the region, as well as to a single, high-resolution simulation for the full storm. It will be shown that switching from a coarse resolution mesh to a fine resolution mesh will lead to an increase in efficiency gains across all switching simulations with the most optimal switch time resulting in the most accurate predictions of water levels as compared to our full high-resolution simulation.
The results of this research will provide valuable contributions to forecasters working tirelessly during hurricane season to produce accurate and efficient predictions of coastal flooding impacts. With this information, real-time forecasts can be delivered sooner to emergency managers for informing evacuation zones, thus saving lives.
AC Poisson (2021). “Identifying the Earliest Signs of Storm Impacts to Improve Hurricane Flooding Forecasts,” North Carolina State University.
 Our recent paper, “Effects of Model Resolution and Coverage on Storm-Driven Coastal Flooding Predictions,” was selected as the Editor’s Choice by the Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal and Ocean Engineering. The chief editor selects a paper from the current issue. The paper is made free with registration and featured on the journal home page for two months, after which it will continue to be featured in the Editor’s Choice Collection.
Our recent paper, “Effects of Model Resolution and Coverage on Storm-Driven Coastal Flooding Predictions,” was selected as the Editor’s Choice by the Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal and Ocean Engineering. The chief editor selects a paper from the current issue. The paper is made free with registration and featured on the journal home page for two months, after which it will continue to be featured in the Editor’s Choice Collection.

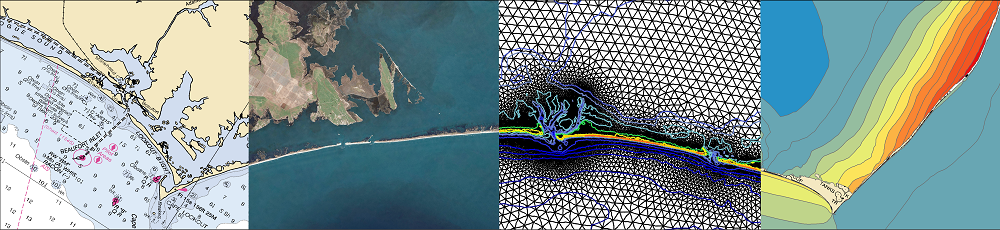
 Predictions of storm surge and flooding require models with higher resolution of coastal regions, to describe fine-scale bathymetric and topographic variations, natural and artificial channels, flow features, and barriers. However, models for real-time forecasting often use a lower resolution to improve efficiency. There is a need to understand how resolution of inland regions can translate to predictive accuracy, but previous studies have not considered differences between models that both represent conveyance into floodplains and are intended to be used in real time. In this study, the effects of model resolution and coverage are explored using comparisons between forecast-ready and production-grade models that both represent floodplains along the US southeast coast, but with typical resolutions in coastal regions of 400 and 50 m, respectively. For two storms that impacted the US southeast coast, it is shown that, although the overall error statistics are similar between simulations on the two meshes, the production-grade model allowed a greater conveyance into inland regions, which improved the tide and surge signals in small channels and increased the inundation volumes between 40% and 60%. Its extended coverage also removed water level errors of 20–40 cm associated with boundary effects in smaller regional models.
Predictions of storm surge and flooding require models with higher resolution of coastal regions, to describe fine-scale bathymetric and topographic variations, natural and artificial channels, flow features, and barriers. However, models for real-time forecasting often use a lower resolution to improve efficiency. There is a need to understand how resolution of inland regions can translate to predictive accuracy, but previous studies have not considered differences between models that both represent conveyance into floodplains and are intended to be used in real time. In this study, the effects of model resolution and coverage are explored using comparisons between forecast-ready and production-grade models that both represent floodplains along the US southeast coast, but with typical resolutions in coastal regions of 400 and 50 m, respectively. For two storms that impacted the US southeast coast, it is shown that, although the overall error statistics are similar between simulations on the two meshes, the production-grade model allowed a greater conveyance into inland regions, which improved the tide and surge signals in small channels and increased the inundation volumes between 40% and 60%. Its extended coverage also removed water level errors of 20–40 cm associated with boundary effects in smaller regional models.
 Hurricanes are devastating natural hazards that often cause damage to the built environment as a result of their loadings, which include storm surge, waves, and wind, often in combination. Modeling these hazards individually and their effects on buildings is a complex process because each loading component within the hazard behaves differently, affecting either the building envelope, the structural system, or the interior contents. Realistic modeling of hurricane effects requires a multihazard approach that considers the combined effects of wind, surge, and waves. Previous studies focused primarily on modeling these hazards individually, with less focus on the multihazard impact on the whole building system made up of the combination of the structure and its interior contents. The analysis resolution used in previous studies did not fully enable hurricane risk assessment through a detailed investigation of the vulnerability at the component-level or subassembly-level (a group of components such as interior contents, structural components, or nonstructural components). To address these research gaps, a robust multihazard hurricane risk analysis model that uses high-resolution hazard, exposure, and vulnerability models was developed. This model uses a novel approach to combine the storm surge and wave fragility functions with a suite of existing wind fragilities to account for structural damage and then combines them with another suite of flood-based fragilities to account for interior content damage. The proposed vulnerability model was applied to the state of North Carolina as an example of a regional-scale assessment to demonstrate the ability of the method to predict damage at the building level across this large spatial domain. This model enables better understanding of the damages caused by hurricanes in coastal regions, thereby setting initial post-impact conditions for community resilience assessment and investigation of recovery policy alternatives.
Hurricanes are devastating natural hazards that often cause damage to the built environment as a result of their loadings, which include storm surge, waves, and wind, often in combination. Modeling these hazards individually and their effects on buildings is a complex process because each loading component within the hazard behaves differently, affecting either the building envelope, the structural system, or the interior contents. Realistic modeling of hurricane effects requires a multihazard approach that considers the combined effects of wind, surge, and waves. Previous studies focused primarily on modeling these hazards individually, with less focus on the multihazard impact on the whole building system made up of the combination of the structure and its interior contents. The analysis resolution used in previous studies did not fully enable hurricane risk assessment through a detailed investigation of the vulnerability at the component-level or subassembly-level (a group of components such as interior contents, structural components, or nonstructural components). To address these research gaps, a robust multihazard hurricane risk analysis model that uses high-resolution hazard, exposure, and vulnerability models was developed. This model uses a novel approach to combine the storm surge and wave fragility functions with a suite of existing wind fragilities to account for structural damage and then combines them with another suite of flood-based fragilities to account for interior content damage. The proposed vulnerability model was applied to the state of North Carolina as an example of a regional-scale assessment to demonstrate the ability of the method to predict damage at the building level across this large spatial domain. This model enables better understanding of the damages caused by hurricanes in coastal regions, thereby setting initial post-impact conditions for community resilience assessment and investigation of recovery policy alternatives.
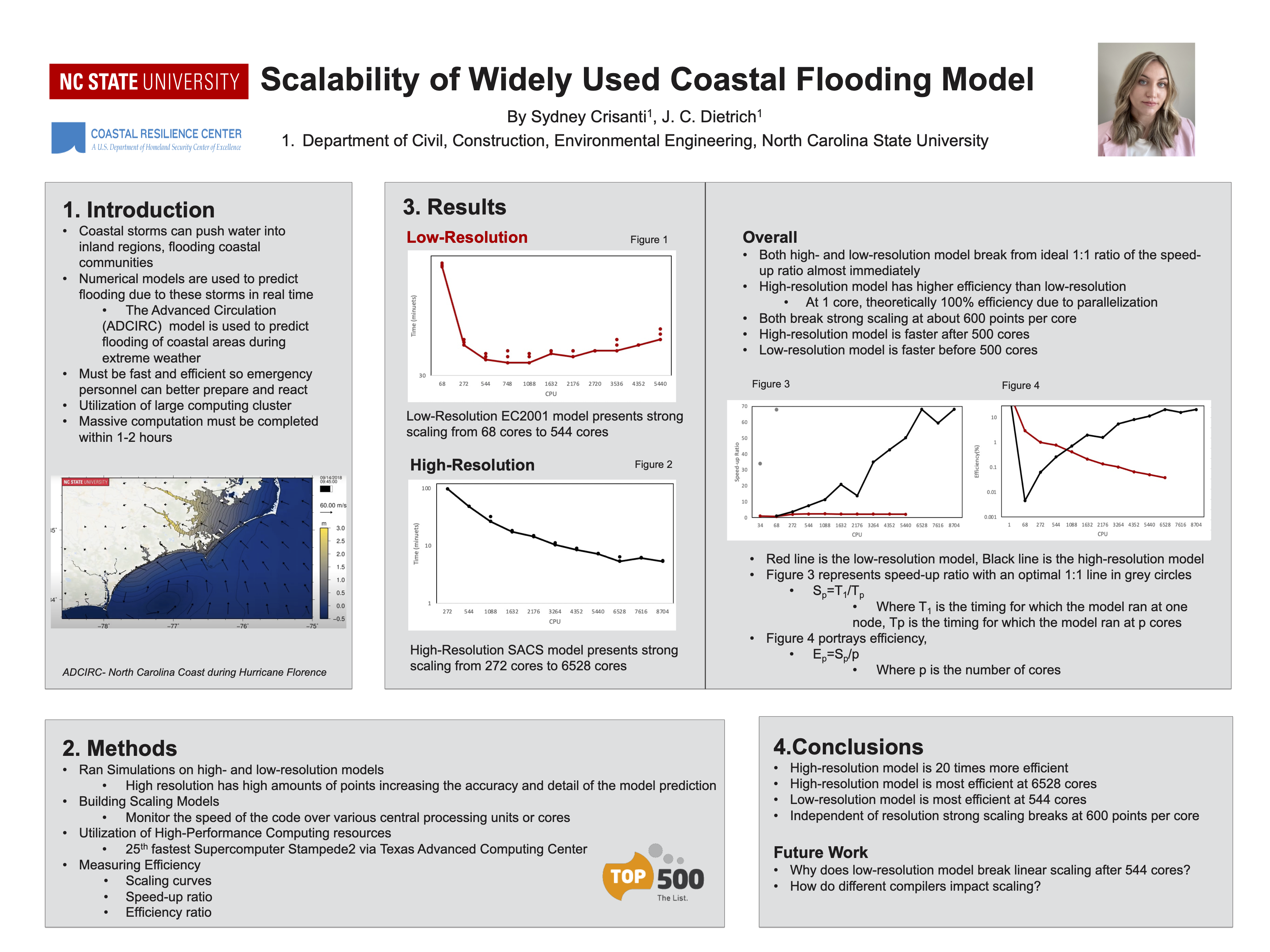
 Storm surge and coastal flooding predictions can require high resolution of critical flow pathways and barriers, typically with simulations using grids/meshes with millions of cells/elements to represent a coastal region. However, the cost of this resolution can slow forecasts during a storm. To add resolution when and where it is needed, previous studies have used adaptive mesh methods, which update resolution at single or multiple cells but which require hierarchies of and thresholds for refinement, and nesting methods, which update resolution at subdomains but which require additional simulations. This research proposes a middle way, in which predictions from a coarse mesh are mapped, mid-simulation, onto a fine mesh with increased resolution near the storm’s projected landfall location. The coarse and fine meshes are pre-developed, thus removing any refinement decisions during the simulation, the solution mapping uses a widely used framework, thus enabling an efficient interpolation, and the same simulation is continued, thus eliminating a separate full-domain simulation. For four historical storms, results show efficiency gains of up to 53 percent, with minimal accuracy losses relative to a static simulation.
Storm surge and coastal flooding predictions can require high resolution of critical flow pathways and barriers, typically with simulations using grids/meshes with millions of cells/elements to represent a coastal region. However, the cost of this resolution can slow forecasts during a storm. To add resolution when and where it is needed, previous studies have used adaptive mesh methods, which update resolution at single or multiple cells but which require hierarchies of and thresholds for refinement, and nesting methods, which update resolution at subdomains but which require additional simulations. This research proposes a middle way, in which predictions from a coarse mesh are mapped, mid-simulation, onto a fine mesh with increased resolution near the storm’s projected landfall location. The coarse and fine meshes are pre-developed, thus removing any refinement decisions during the simulation, the solution mapping uses a widely used framework, thus enabling an efficient interpolation, and the same simulation is continued, thus eliminating a separate full-domain simulation. For four historical storms, results show efficiency gains of up to 53 percent, with minimal accuracy losses relative to a static simulation.
 One of the most unpredictable and deadly parts of a coastal storm is the storm surge, which can cause devastating flooding of coastal regions, and can result in loss of property and life. Storm surge is a result of winds pushing water from the nearshore ocean to rise above regular tide levels. Storm surge can have a short duration; elevated water levels are limited to when the storm winds are strongest at the coast, typically for a few hours as the storm makes landfall. This short duration is a challenge for predictions of when storm surge will start, how long it will persist, and which regions will be flooded.
One of the most unpredictable and deadly parts of a coastal storm is the storm surge, which can cause devastating flooding of coastal regions, and can result in loss of property and life. Storm surge is a result of winds pushing water from the nearshore ocean to rise above regular tide levels. Storm surge can have a short duration; elevated water levels are limited to when the storm winds are strongest at the coast, typically for a few hours as the storm makes landfall. This short duration is a challenge for predictions of when storm surge will start, how long it will persist, and which regions will be flooded.
 This research will explore the arrival of storm effects for Florence, which made landfall along the North Carolina coast during September 2018. It is an ideal storm for this research as its track was shore-normal, and thus its coastal effects increased as it approached landfall. This will allow for investigating the most optimal switch by focusing on a single switch between a lower-resolution mesh to a higher-resolution mesh. The switches will be initiated by several triggers, including wind speeds and water levels at the coast and inland locations, and with several lead times, including near and several days before landfall. Model performance will be quantified via comparisons to observations of storm effects in the region, as well as to a single, high-resolution simulation for the full storm. It will be shown that switching from a coarse resolution mesh to a fine resolution mesh will lead to an increase in efficiency gains across all switching simulations with the most optimal switch time resulting in the most accurate predictions of water levels as compared to our full high-resolution simulation.
This research will explore the arrival of storm effects for Florence, which made landfall along the North Carolina coast during September 2018. It is an ideal storm for this research as its track was shore-normal, and thus its coastal effects increased as it approached landfall. This will allow for investigating the most optimal switch by focusing on a single switch between a lower-resolution mesh to a higher-resolution mesh. The switches will be initiated by several triggers, including wind speeds and water levels at the coast and inland locations, and with several lead times, including near and several days before landfall. Model performance will be quantified via comparisons to observations of storm effects in the region, as well as to a single, high-resolution simulation for the full storm. It will be shown that switching from a coarse resolution mesh to a fine resolution mesh will lead to an increase in efficiency gains across all switching simulations with the most optimal switch time resulting in the most accurate predictions of water levels as compared to our full high-resolution simulation.