Category Archives: Models
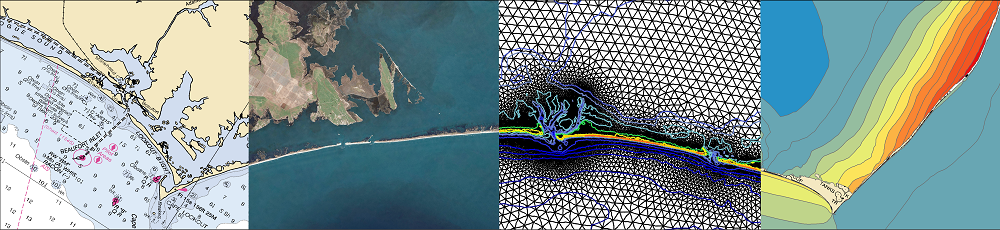
Coupling of Inlet-Scale Erosion and Region-Scale Flooding Predictions
JC Dietrich. “Coupling of Inlet-Scale Erosion and Region-Scale Flooding Predictions.” U.S. Coastal Research Program, Storm Processes and Impacts Workshop, Technology Challenge, 2018/09/23 to 2019/09/22, $59,950 (Dietrich: $59,950).
Presentation: PREEVENTS PI Meeting
News: Storm Surge Modeling during Hurricane Florence
Hurricane Florence Coverage from Around the State
Hurricane Florence, which is now a Category 2 storm, continues to bear down on the Carolina coast. The National Weather Service says it is likely to be “the storm of a lifetime” for certain portions of that coastline. Officials have ordered the evacuation of over 1 million people from the coasts of North and South Carolina. … Stasio is joined by Casey Dietrich, a professor in North Carolina State University’s Department of Civil, Construction and Environmental Engineering and leader of its Coastal and Computational Hydraulics Team. Dietrich explains the models currently being refined to help predict and plan for hurricanes and their effects on coastlines.
For this episode of The State of Things, the full-length podcast is embedded below. The interview with Casey Dietrich starts at about the 37-minute mark. It was great to describe our projects with DHS, NSF, and NC Sea Grant as part of this episode about Hurricane Florence.
Dissertation Defense: Rosemary Cyriac
Variability in Coastal Flooding Predictions due to Forecast Errors during Hurricane Arthur
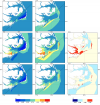 Storm surge prediction models rely on an accurate representation of the wind conditions. In this paper, we examine the sensitivity of surge predictions to forecast uncertainties in the track and strength of a storm (storm strength is quantified by the power dissipation of the associated wind field). This analysis is performed using Hurricane Arthur (2014), a Category 2 hurricane, which made landfall along the North Carolina (NC) coast in early July 2014. Hindcast simulations of a coupled hydrodynamic-wave model are performed on a large unstructured mesh to analyze the surge impact of Arthur along the NC coastline. The effects of Arthur are best represented by a post-storm data assimilated wind product with parametric vortex winds providing a close approximation. Surge predictions driven by forecast advisories issued by the National Hurricane Center (NHC) during Arthur are analyzed. The storm track predictions from the NHC improve over time. However, successive advisories predict an unrealistic increase in the storm’s strength. Due to these forecast errors, the global root mean square errors of the predicted wind speeds and water levels increase as the storm approaches landfall. The relative impacts of the track and strength errors on the surge predictions are assessed by replacing forecast storm parameters with the best known post-storm information about Arthur. In a “constant track” analysis, Arthur’s post storm determined track is used in place of the track predictions of the different advisories but each advisory retains its size and intensity predictions. In a “constant storm strength” analysis, forecast wind and pressure parameters are replaced by corresponding parameters extracted from the post storm analysis while each advisory retains its forecast storm track. We observe a strong correlation between the forecast errors and the wind speed predictions. However, the correlation between these errors and the forecast water levels is weak signifying a non-linear response of the shallow coastal waters to meteorological forcing.
Storm surge prediction models rely on an accurate representation of the wind conditions. In this paper, we examine the sensitivity of surge predictions to forecast uncertainties in the track and strength of a storm (storm strength is quantified by the power dissipation of the associated wind field). This analysis is performed using Hurricane Arthur (2014), a Category 2 hurricane, which made landfall along the North Carolina (NC) coast in early July 2014. Hindcast simulations of a coupled hydrodynamic-wave model are performed on a large unstructured mesh to analyze the surge impact of Arthur along the NC coastline. The effects of Arthur are best represented by a post-storm data assimilated wind product with parametric vortex winds providing a close approximation. Surge predictions driven by forecast advisories issued by the National Hurricane Center (NHC) during Arthur are analyzed. The storm track predictions from the NHC improve over time. However, successive advisories predict an unrealistic increase in the storm’s strength. Due to these forecast errors, the global root mean square errors of the predicted wind speeds and water levels increase as the storm approaches landfall. The relative impacts of the track and strength errors on the surge predictions are assessed by replacing forecast storm parameters with the best known post-storm information about Arthur. In a “constant track” analysis, Arthur’s post storm determined track is used in place of the track predictions of the different advisories but each advisory retains its size and intensity predictions. In a “constant storm strength” analysis, forecast wind and pressure parameters are replaced by corresponding parameters extracted from the post storm analysis while each advisory retains its forecast storm track. We observe a strong correlation between the forecast errors and the wind speed predictions. However, the correlation between these errors and the forecast water levels is weak signifying a non-linear response of the shallow coastal waters to meteorological forcing.
Cyberinfrastructure for Enhancing Interdisciplinary Engagement in Coastal Risk Management Research
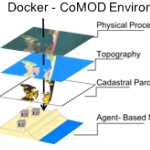 Tackling critical questions often requires the collaboration of researchers from different disciplines or institutions. Coastal hazards research is necessarily interdisciplinary and multi- methodological and often requires a team of researchers, due to its combination of storm-induced changes to the coastal environment, the effects of these changes on built infrastructure, and the combined effects on decision-making for individuals and communities. This paper introduces an interdisciplinary coastal hazard risk model that combines high resolution geospatial data, storm impact forecasts, and an agent-based model in the analysis, and then describes the model’s implementation in a data science cyberinfrastructure. Lessons learned and limitations are also outlined.
Tackling critical questions often requires the collaboration of researchers from different disciplines or institutions. Coastal hazards research is necessarily interdisciplinary and multi- methodological and often requires a team of researchers, due to its combination of storm-induced changes to the coastal environment, the effects of these changes on built infrastructure, and the combined effects on decision-making for individuals and communities. This paper introduces an interdisciplinary coastal hazard risk model that combines high resolution geospatial data, storm impact forecasts, and an agent-based model in the analysis, and then describes the model’s implementation in a data science cyberinfrastructure. Lessons learned and limitations are also outlined.