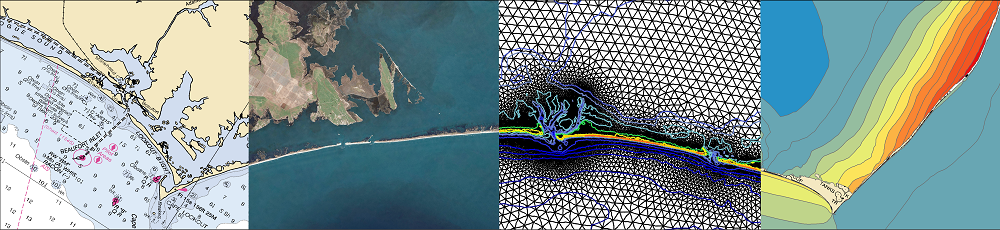
This paper investigates model response sensitivities to mesh resolution, topographical details, bottom friction formulations, the interaction of wind waves and circulation, and nonlinear advection on tidal and hurricane surge and wave processes at the basin, shelf, wetland, and coastal channel scales within the Gulf of Mexico. Tides in the Gulf of Mexico are modestly energetic processes, whereas hurricane surge and waves are highly energetic. The unstructured-mesh, coupled wind-wave and circulation modeling system, SWAN+ADCIRC, is implemented to generate modeled tidal harmonic constituents and hurricane waves and surge for a Hurricane Ike (2008) hindcast. In the open ocean, mesh resolution requirements are less stringent in achieving accurate tidal signals or matching hurricane surge and wave responses; however, coarser resolution or the absence of intertidal zones decreases accuracy along protected nearshore and inland coastal areas due to improper conveyance and/or lateral attenuation. Bottom friction formulations are shown to have little impact on tidal signal accuracy, but hurricane surge is much more sensitive, especially in shelf waters, where development of a strong shore-parallel current is essential to the development of Ike’s geostrophic setup. The spatial and temporal contributions of wave radiation stress gradients and nonlinear advection were charted for Ike. Nonlinear advection improves model performance by capturing an additional 10–20 cm of geostrophic setup and increasing resonant cross-shelf waves by 30–40 cm. Wave radiation stress gradients improve performance at coastal stations by adding an extra 20–40 cm to water levels.
PC Kerr, RC Martyr, AS Donahue, ME Hope, JJ Westerink, RA Luettich Jr, AB Kennedy, JC Dietrich, CN Dawson, HJ Westerink (2013). “U.S. IOOS Coastal and Ocean Modeling Testbed: Evaluation of Tide, Wave, and Hurricane Surge Response Sensitivities to Mesh Resolution and Friction in the Gulf of Mexico.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 118, 4633-4661, DOI: 10.1002/jgrc.20305.
 This paper investigates model response sensitivities to mesh resolution, topographical details, bottom friction formulations, the interaction of wind waves and circulation, and nonlinear advection on tidal and hurricane surge and wave processes at the basin, shelf, wetland, and coastal channel scales within the Gulf of Mexico. Tides in the Gulf of Mexico are modestly energetic processes, whereas hurricane surge and waves are highly energetic. The unstructured-mesh, coupled wind-wave and circulation modeling system, SWAN+ADCIRC, is implemented to generate modeled tidal harmonic constituents and hurricane waves and surge for a Hurricane Ike (2008) hindcast. In the open ocean, mesh resolution requirements are less stringent in achieving accurate tidal signals or matching hurricane surge and wave responses; however, coarser resolution or the absence of intertidal zones decreases accuracy along protected nearshore and inland coastal areas due to improper conveyance and/or lateral attenuation. Bottom friction formulations are shown to have little impact on tidal signal accuracy, but hurricane surge is much more sensitive, especially in shelf waters, where development of a strong shore-parallel current is essential to the development of Ike’s geostrophic setup. The spatial and temporal contributions of wave radiation stress gradients and nonlinear advection were charted for Ike. Nonlinear advection improves model performance by capturing an additional 10–20 cm of geostrophic setup and increasing resonant cross-shelf waves by 30–40 cm. Wave radiation stress gradients improve performance at coastal stations by adding an extra 20–40 cm to water levels.
This paper investigates model response sensitivities to mesh resolution, topographical details, bottom friction formulations, the interaction of wind waves and circulation, and nonlinear advection on tidal and hurricane surge and wave processes at the basin, shelf, wetland, and coastal channel scales within the Gulf of Mexico. Tides in the Gulf of Mexico are modestly energetic processes, whereas hurricane surge and waves are highly energetic. The unstructured-mesh, coupled wind-wave and circulation modeling system, SWAN+ADCIRC, is implemented to generate modeled tidal harmonic constituents and hurricane waves and surge for a Hurricane Ike (2008) hindcast. In the open ocean, mesh resolution requirements are less stringent in achieving accurate tidal signals or matching hurricane surge and wave responses; however, coarser resolution or the absence of intertidal zones decreases accuracy along protected nearshore and inland coastal areas due to improper conveyance and/or lateral attenuation. Bottom friction formulations are shown to have little impact on tidal signal accuracy, but hurricane surge is much more sensitive, especially in shelf waters, where development of a strong shore-parallel current is essential to the development of Ike’s geostrophic setup. The spatial and temporal contributions of wave radiation stress gradients and nonlinear advection were charted for Ike. Nonlinear advection improves model performance by capturing an additional 10–20 cm of geostrophic setup and increasing resonant cross-shelf waves by 30–40 cm. Wave radiation stress gradients improve performance at coastal stations by adding an extra 20–40 cm to water levels.
 This paper investigates model response sensitivities to mesh resolution, topographical details, bottom friction formulations, the interaction of wind waves and circulation, and nonlinear advection on tidal and hurricane surge and wave processes at the basin, shelf, wetland, and coastal channel scales within the Gulf of Mexico. Tides in the Gulf of Mexico are modestly energetic processes, whereas hurricane surge and waves are highly energetic. The unstructured-mesh, coupled wind-wave and circulation modeling system, SWAN+ADCIRC, is implemented to generate modeled tidal harmonic constituents and hurricane waves and surge for a Hurricane Ike (2008) hindcast. In the open ocean, mesh resolution requirements are less stringent in achieving accurate tidal signals or matching hurricane surge and wave responses; however, coarser resolution or the absence of intertidal zones decreases accuracy along protected nearshore and inland coastal areas due to improper conveyance and/or lateral attenuation. Bottom friction formulations are shown to have little impact on tidal signal accuracy, but hurricane surge is much more sensitive, especially in shelf waters, where development of a strong shore-parallel current is essential to the development of Ike’s geostrophic setup. The spatial and temporal contributions of wave radiation stress gradients and nonlinear advection were charted for Ike. Nonlinear advection improves model performance by capturing an additional 10–20 cm of geostrophic setup and increasing resonant cross-shelf waves by 30–40 cm. Wave radiation stress gradients improve performance at coastal stations by adding an extra 20–40 cm to water levels.
This paper investigates model response sensitivities to mesh resolution, topographical details, bottom friction formulations, the interaction of wind waves and circulation, and nonlinear advection on tidal and hurricane surge and wave processes at the basin, shelf, wetland, and coastal channel scales within the Gulf of Mexico. Tides in the Gulf of Mexico are modestly energetic processes, whereas hurricane surge and waves are highly energetic. The unstructured-mesh, coupled wind-wave and circulation modeling system, SWAN+ADCIRC, is implemented to generate modeled tidal harmonic constituents and hurricane waves and surge for a Hurricane Ike (2008) hindcast. In the open ocean, mesh resolution requirements are less stringent in achieving accurate tidal signals or matching hurricane surge and wave responses; however, coarser resolution or the absence of intertidal zones decreases accuracy along protected nearshore and inland coastal areas due to improper conveyance and/or lateral attenuation. Bottom friction formulations are shown to have little impact on tidal signal accuracy, but hurricane surge is much more sensitive, especially in shelf waters, where development of a strong shore-parallel current is essential to the development of Ike’s geostrophic setup. The spatial and temporal contributions of wave radiation stress gradients and nonlinear advection were charted for Ike. Nonlinear advection improves model performance by capturing an additional 10–20 cm of geostrophic setup and increasing resonant cross-shelf waves by 30–40 cm. Wave radiation stress gradients improve performance at coastal stations by adding an extra 20–40 cm to water levels.